The combination of reality capture and Building Information Modeling (BIM) creates more streamlined design and construction processes as well as more efficient asset management. Both processes mark advancements in how buildings, infrastructure and other spaces are designed and maintained by multi-disciplinary teams.
Reality capture is a visualization or scanning process that maps and measures a space for the creation of 3D models. While the underlying concept of reality capture remains the same as traditional methods of site surveillance, technological advancements have made the process of detailed data collection more rigorous and therefore more useful for BIM.
Here are a few details about reality capture and how it integrates into BIM.
How is Reality Capture Done?
Essentially, reality capture is the process of doing a comprehensive scan of a site. This process is possible because of the increasing availability of UAVs (Unmanned Ariel Vehicles), or drones. A camera or laser is mounted on a UAV, which flies around a site or building collecting data. The data points, also known as point clouds, are then processed by photogrammetry software to make the 3D data BIM capable.
Photogrammetry refers to the process of digitally stitching together overlapping images. This could be done with photos that were taken manually, but if you become a BIM technician you will appreciate the accuracy and speed of the reality capture process for the photogrammetry component of creating 3D models.
Reality Capture is Quicker and More Accurate
After you take BIM courses you will have hands-on knowledge about 3D models and how much information is necessary to create them. Further, BIM is able to include information about the feasibility of a project, an estimation of cost and time, as well as any potential risks or dangers involved. Reality capture is a scanning process designed to make the collection of all of this data more efficient and less labour intensive.
Typically, workers have to visit a site several times using levels, tape measures, theodolites and other tools to collect data. The reality capture process collects information about the site faster and yields data points needed for BIM that are more accurate and complete.
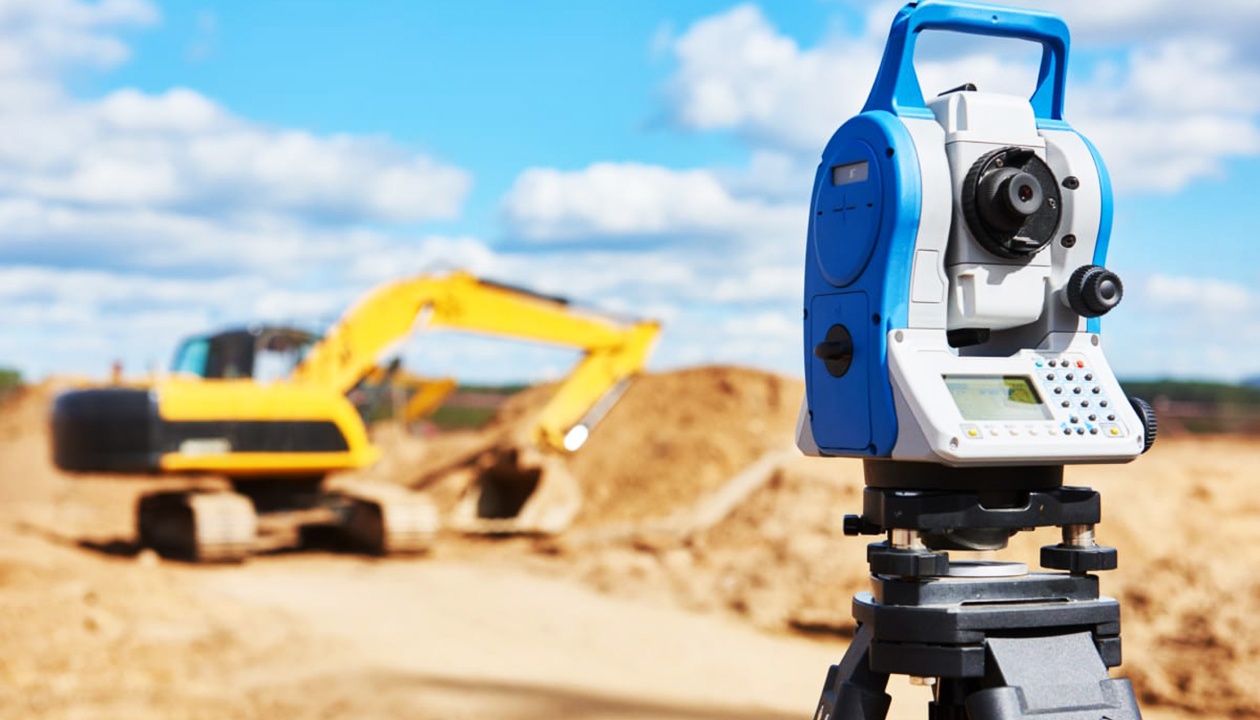

A theodolite is a tool used to measure angles between points on horizontal and vertical axes
Learn BIM to Understand the Importance of Reality Capture
When you learn BIM you will be making an investment in your future career. You will also learn that 3D information like shape and dimension are only two of the many elements involved in BIM. The kind of geometric information that reality capture generates is essential for BIM, but BIM’s functions don’t end there.
Among other capabilities, BIM is a process that is able to integrate information about different phases of a project over time, making a 3D model into a 4D model. In the same way reality capture can provide information that creates an initial model for a project, it can also provide information about design and construction progress and conditions at the building site. For example, instead of construction workers surveying a multi-story building manually, reality capture tools can gather that data and update BIM projects comprehensively at every phase. For these and other reasons, employers in the architecture, engineering, and construction fields are increasingly on the lookout for professionals with BIM training.
Want to learn more about BIM?
Your career awaits.